

Plastic injection molding has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, providing a cost-effective and efficient solution for creating a wide range of plastic products. From automotive components to consumer goods, the process of plastic injection molding offers unmatched versatility and design flexibility. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of plastic injection molding, its advantages, materials used, equipment involved, design considerations, quality control measures, sustainability aspects, industries benefiting from this process, and future trends.
Introduction to Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding refers to a manufacturing technique where liquid plastic material is forcefully injected into a mold cavity at high pressure. Once the plastic cools and solidifies, the mold is opened, and the finished product is ejected. This process has gained immense popularity due to its ability to produce complex shapes, high production volumes, and consistent quality.
Plastic injection molding finds applications in various industries, including automotive, electronics, packaging, medical, and more. It enables the production of a wide range of products, such as housings, containers, caps, toys, and intricate components with intricate geometries.
The Process of Plastic Injection Molding
The process of plastic injection molding consists of several steps that ensure the successful transformation of raw materials into the desired product. Let's explore these steps:
Clamping: The mold halves are securely closed and held together by a clamping unit, ensuring a tight seal.
Injection: The molten plastic material, typically in the form of pellets, is injected into the mold cavity through a runner system under high pressure.
Cooling: The injected plastic cools and solidifies within the mold, taking the shape of the cavity. Cooling time is determined by the material and part thickness.
Mold Opening: Once the plastic has sufficiently cooled, the mold is opened, separating the two halves.
Ejection: The finished product is ejected from the mold using ejector pins, and the cycle is repeated for the next part.
Advantages of Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding offers numerous advantages over alternative manufacturing processes. Let's delve into some of its key benefits:
Cost-effectiveness
Plastic injection molding allows for high-volume production, reducing the per-unit cost significantly. The automated nature of the process, coupled with the ability to use multi-cavity molds, ensures efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Versatility and Design Flexibility
One of the standout features of plastic injection molding is its versatility in creating intricate and complex designs. The process enables the production of parts with varying thicknesses, undercuts, and complex geometries, giving designers unparalleled freedom.
Efficiency and Productivity
With rapid cycle times and the potential for automation, plastic injection molding offers exceptional efficiency and productivity. High-speed injection molding machines coupled with optimized mold designs allow for quick production cycles, meeting the demands of high-volume manufacturing.
Materials Used in Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding utilizes a wide range of thermoplastic and thermosetting materials. The choice of material depends on the desired properties, application requirements, and cost considerations. Some commonly used plastic materials include:
Polypropylene (PP)
Polyethylene (PE)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Polystyrene (PS)
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Nylon (PA)
Polycarbonate (PC)
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
When selecting a material, factors such as strength, flexibility, chemical resistance, and temperature resistance must be taken into account.
Equipment and Tools in Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding relies on specialized equipment and tools to ensure precise and efficient production. The key components of the equipment include:
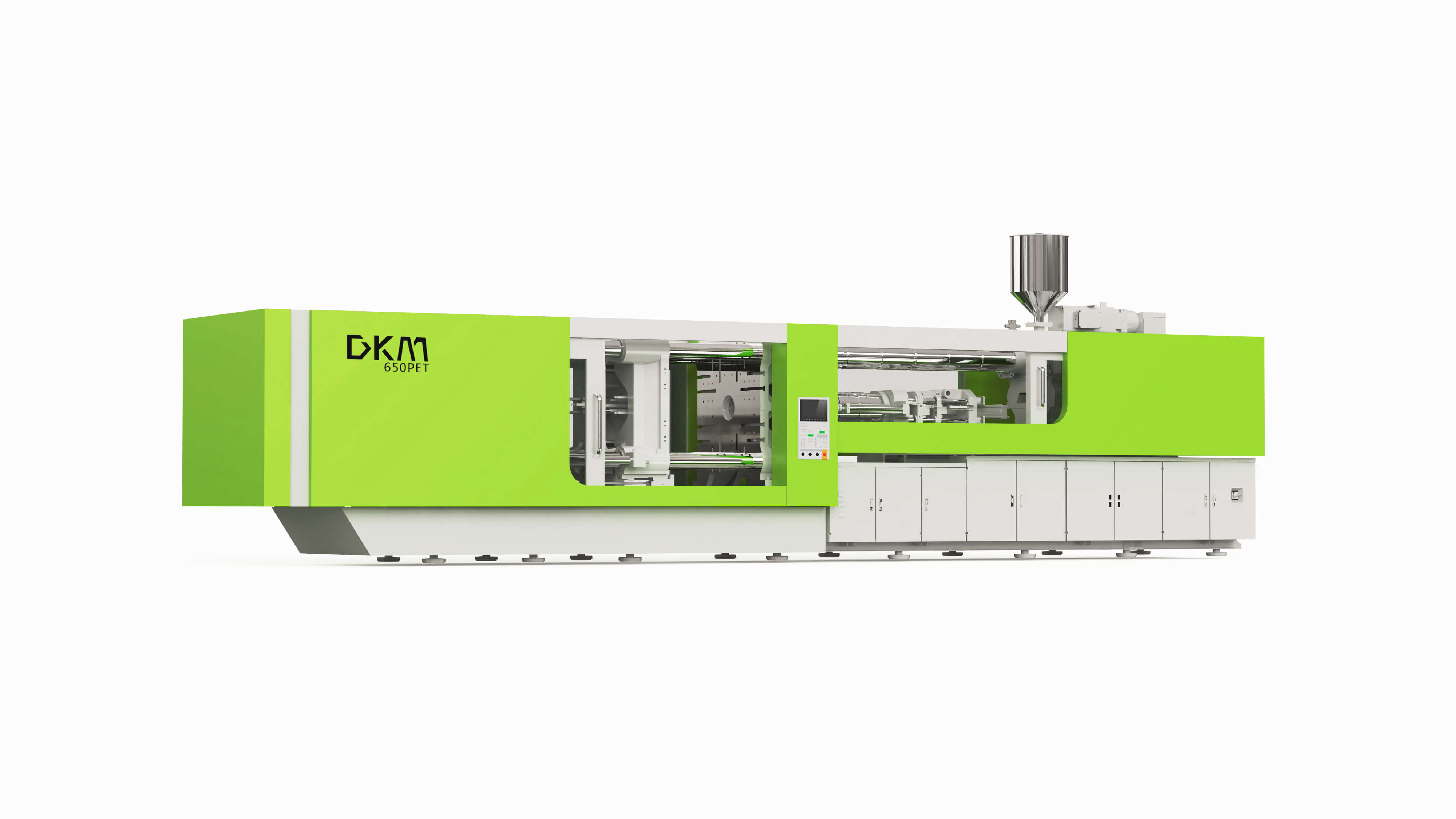
Injection Molding Machines
Injection molding machines vary in size and complexity, ranging from small benchtop machines to large-scale industrial systems. These machines consist of a hopper, an injection unit, a clamping unit, and a control system. Modern machines often incorporate advanced features like servo-driven systems for improved precision and energy efficiency.
Mold Design and Construction
Molds are crucial in plastic injection molding as they define the final shape and quality of the product. Mold design involves careful consideration of factors such as part geometry, gating system, cooling channels, and ejection mechanisms. The molds are typically made from steel or aluminum alloys, depending on the production volume and material requirements.
Design Considerations for Plastic Injection Molding
Designing parts for plastic injection molding requires attention to specific guidelines to ensure successful production. Key considerations include:
Wall Thickness and Draft Angles
Maintaining consistent wall thickness throughout the part helps prevent defects like warping and sink marks. Additionally, incorporating draft angles on vertical surfaces facilitates easy ejection from the mold.
Gate and Runner Design
The gate is the point through which the molten plastic enters the mold cavity. Proper gate design is crucial to ensure uniform filling and prevent issues like flow marks or part distortion. The runner system, consisting of channels that deliver plastic to the cavities, must be carefully designed to optimize material flow and minimize waste.
Quality Control in Plastic Injection Molding
Maintaining quality standards is essential in plastic injection molding to ensure the production of defect-free parts. Quality control measures include:
Inspection and Testing Methods
Various inspection techniques such as visual inspection, dimensional measurement, and functional testing are employed to verify part quality. Advanced technologies like coordinate measuring machines (CMM) and non-destructive testing (NDT) help detect potential defects.
Defect Prevention and Troubleshooting
Addressing common defects such as flash, sink marks, short shots, or voids requires a thorough understanding of the molding process. Implementing preventive measures and troubleshooting techniques minimizes the occurrence of defects and maximizes product quality.
Sustainability in Plastic Injection Molding
In recent years, sustainability has gained prominence in the manufacturing industry. Plastic injection molding can contribute to sustainable practices through the following measures:
Recycling and Waste Reduction
Efforts to recycle and reuse plastic materials reduce the environmental impact of plastic injection molding. Proper segregation of waste, use of recycled materials, and regrinding of excess plastic help minimize waste generation.
Eco-friendly Materials and Practices
Exploring alternative materials, such as biodegradable or compostable plastics, supports eco-friendly practices. Additionally, optimizing energy usage, implementing efficient cooling systems, and reducing water consumption contribute to sustainable manufacturing.
Industries Utilizing Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding plays a crucial role in several industries, including:
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector extensively uses plastic injection molding for producing components such as dashboards, bumpers, interior trims, and connectors. The process's ability to meet strict quality standards and produce lightweight parts makes it highly valuable in this industry.
Consumer Goods Industry
Plastic injection molding enables the production of a wide range of consumer goods, including household appliances, electronic enclosures, packaging containers, and toys. The process allows for intricate designs, vibrant colors, and durable products that meet consumer expectations.
Medical and Healthcare Industry
In the medical field, precision and quality are of utmost importance. Plastic injection molding provides the means to produce medical devices, equipment components, and disposable items with strict adherence to hygiene and safety regulations.
Future Trends in Plastic Injection Molding
As technology continues to advance, plastic injection molding is poised to benefit from several exciting developments. Here are some anticipated future trends in the industry:
Advancements in Technology
Innovations like the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms into injection molding machines are expected to enhance process control, improve quality, and optimize production efficiency. Predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring systems will enable proactive maintenance and minimize machine downtime.
Industry Developments and Innovations
Ongoing research and development efforts aim to introduce new materials with enhanced properties, improved biodegradability, and recyclability. Additive manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing, are being integrated with injection molding to enable rapid prototyping and production of customized parts.
In conclusion, plastic injection molding has transformed the manufacturing landscape, enabling the production of intricate, high-quality plastic products in various industries. The process offers advantages in terms of cost-effectiveness, design flexibility, and productivity. By considering design guidelines, selecting suitable materials, and implementing quality control measures, manufacturers can ensure the successful execution of plastic injection molding projects. As the industry continues to evolve, embracing sustainable practices and embracing technological advancements will further enhance the capabilities and applications of plastic injection molding.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is plastic injection molding suitable for small-scale production?
Yes, plastic injection molding can be used for small-scale production. The process is scalable and can accommodate both high and low production volumes.
Q: How long does the plastic injection molding process take?
The duration of the process depends on factors such as part complexity, material, and machine capabilities. It can range from a few seconds to a few minutes.
Q: What are the limitations of plastic injection molding?
Some limitations include high initial tooling costs, longer lead times for mold production, and restrictions on part size and thickness.
Q: Can recycled materials be used in plastic injection molding?
Yes, recycled materials can be used in plastic injection molding. By regrinding and reprocessing plastic waste, manufacturers can reduce their environmental footprint.
Q: What are some alternative manufacturing processes to plastic injection molding?
Alternative processes include blow molding, rotational molding, thermoforming, and extrusion molding. Each process has its own strengths and suitability for specific applications.